3JCN - The Simplest Music Notation
PLUS, MINUS, and NATURAL NOTES
(or SHARP, FLAT, and NATURAL NOTES)
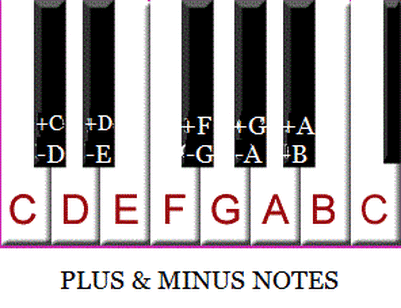
It's easier to understand plus/minus notes by take a look at piano keys as the picture at the bottom of this page.
There are 7 base note names, A - B - C - D - E - F - G (white) and 5 black notes in each pattern (octave) as picture below.
Each of these black notes can be called a plus (+) or minus (-). For example, the first black key on the left can be called "+C" or "- D"; Note "E" can be called "- F", etc.
In short, plus (or sharp) note is the next note on the right (higher pitch, higher frequency).
Minus (or flat) note is the next note on the left (lower pitch, lower frequency).
Natural note is an accidental which cancels previous accidentals and represents the unaltered pitch of a note
Examples: +C (sharp note) -D (flat note) oA (natural note)
These names are used over and over again and change tone in a mathematical relationship. Two notes next together creates one semitone (example: C and +C; or E and F; or B and C; or -B and B...). Two semitone next together creates one tone (example: C and D; F and G; -B and C; ...)
This concept of tome and semitone exist for other musical instruments. When you study positions of notes on your instruments, you can see a slightly different with piano (no black and white).
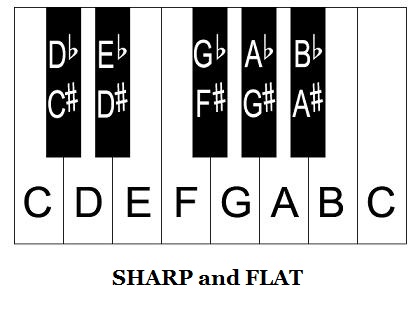
There are 7 base note names, A - B - C - D - E - F - G (white) and 5 black notes in each pattern (octave) as picture below.
Each of these black notes can be called a plus (+) or minus (-). For example, the first black key on the left can be called "+C" or "- D"; Note "E" can be called "- F", etc.
In short, plus (or sharp) note is the next note on the right (higher pitch, higher frequency).
Minus (or flat) note is the next note on the left (lower pitch, lower frequency).
Natural note is an accidental which cancels previous accidentals and represents the unaltered pitch of a note
Examples: +C (sharp note) -D (flat note) oA (natural note)
These names are used over and over again and change tone in a mathematical relationship. Two notes next together creates one semitone (example: C and +C; or E and F; or B and C; or -B and B...). Two semitone next together creates one tone (example: C and D; F and G; -B and C; ...)
This concept of tome and semitone exist for other musical instruments. When you study positions of notes on your instruments, you can see a slightly different with piano (no black and white).